[ad_1]
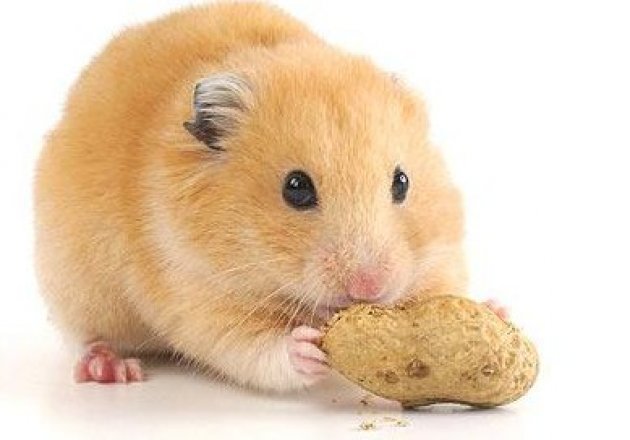
Hamsters were discovered 70 years ago in the Syrian Desert. They have quickly become popular household pets due to their friendly nature and adaptability.
When setting up a habitat, note that there is not such thing as too big of an environment. The cage should be as big as possible considering it is where the pet will be spending most of its time. Make it interesting and comfortable. The cage should be at least 2 square feet, and the spacing between bars should be a minimum of an an inch as any larger, and the hamster fall through. Aquariums can also be used for habitats. They should be well ventilated and have screen lid. The commercialized colorful plastic cages do not make good habitats due to their poor ventilation and difficulty to clean.
Bedding can be made from recycled paper materials or woods which do not contain scents. Aspen is also viable. Cedar and pine shavings are toxic to animals and that should never bee used. In addition, sawdust, corn cob, chlorophyll, and cat litter make poor beddings as well.
Hamsters need private places within their cage where they can feel secure. Empty oatmeal cans or tissue boxes perform this function, and the hamster will have something to nibble at as well. Since the hamster will most likely try to ingest their home, do not place any soft plastics in the environment. PVC plastic is generally safe as it is tough enough to withstanding chewing. Unscented toilet paper can be used as nesting material. Be wary of the commercial "fluff" as it has the potential to block intestines if swallowed.
Hamsters should have a constant supply of water and food. The food should contain a minimum of 16 percent protein and not have molasses. Avoid mixes which include ethoxyquin. A hamster's diet should have a mixture of vegetables, fruits, protein, and whole grains. They will eat a variety of vegetables including squash, spinach, red and green peppers, peas, parsley, cucumber, celery, cauliflower, carrots, broccoli, basis, avocado, and asparagus. Fruits can be given occasionally, but only to Syrian hamsters. Because of the high rate of diabetes in dwarf hamsters, fruit should be avoided. Hamsters may also have in small quantities whole wheat, pumpkin seeds, tofu, and hard-boiled eggs. Avoid garlic, raw beans, dried corn, iceberg lettuce, chocolate, processed food, anything with a high sugar or salt content. Mineral or salt wheels are not healthy.
For more information caring for hamsters, consult Houston Veterinarian Clinics today.
[ad_2]
Source by Joseph Devine